Online Training Institute
Process Piping Online
- 30 Days Training
- Project Work With Next Trends
- Placement Assistance.
The Course enables the entry level and working engineers to understand the basics, different systems used in Chemical, Civil, Electrical, Equipment, Structural, Firefighting and Instrumentation.
1. Introduction of piping Engineering
- Definition of Pipe and piping
- Application of Piping
- Introduction of Process Plants
- Differences between tube, Pipe and its application.
- Piping Standards.
- Line specification and its importance.
- Pipe ends, joining types and application.
- Pressure class rating.
- NPS, DN and OD.
2. Pipe Manufacturing Methods
- Seam pipe
- Seamless Pipe
- Spiral Pipe
- U.O Pipe
3. Valves : ASME Standards
- Applications.
- Operation.
- Orientation.
- Drawing symbols.
- Dimensions.
- Pressure Drop.
- Back flow.
- Standards.
- Selections.
- Specifications.
- Types of valve – Gate, globe, ball, plug, pinch, diaphragm, PSV, PRV, Butterfly, NRV, Diverting, mixing, knife, etc.,
4.Flanges
- Pipe Flange
- Joining Methods
- Stub – In
- Stub – On
- Stub – End
- Flange standards
- Applications
- Drawing symbols
- Dimensions and pressure class rating selection
- Types of flanges (Slip on flange, Threaded, Orifice, Weld neck, Socket, Blind, Reduced, Lap joint, Flange, Spades & spectacle Blind
5.Fittings
- Standards
- Dimensions
- Symbolic representations.
- Applications.
- Design concepts.
- Specification.
- Types. (90° LR & SR,45° LR & SR.).
- Bends – 180° LR & SR , miter bends.
- Branch connections – SS.
- Straight (Equal Tees, Unequal Tees).
- Cross – Tees.
- Reducers /Expands. (Concentric, Eccentric).
- Olets( Weldolets, Sockets, Threadolets, Latrolets, Elbolets, Sweepolets,Thermolets, Flageolets etc.).
- Couplings.(Full, Half ,Reducing, Unions).
- Special fittings. (Traps, Expansion bellows, Expansion loops, Strainers,)
6.Gaskets.
- Types of gaskets.
- Selection @ process fluids.
- Specification.
- Standards.
- Types of flange facings.(Flat, Raised face, RTJ.)
- Flange face finishing.(Tangent grooves, Radio graphics and Concentric gloves.).
7.Gaskets indication color representation
- Drawing generations.
- Straight isometric.
- Single rolling isometric.
- Double rolling isometric.
- Drawings Extractions.
8. Detailed MTO’s.
- Process Equipment (Representation, Standards, Application).
- Static Equipment ( Horizontal Vessel, Vertical Vessel, Storage Tank, Heat exchangers ).
- Rotary Equipment ( Pumps, Compressors, Blowers, Turbines, Reactors and Distillery Columns, Etc. )
9.PFD and P&ID’s.
- Process Flow Diagram (PFD).
- Piping and Instrumentation Diagram (P&ID).
- Development of P&ID from formulae.
- Symbolic representation.
- Process flow.
- Reading of P&ID ( Line list, Equipment list ).
- Development of piping diagrams with PFD and P&ID.
- Instruments, loop diagrams, symbols.
- Utility flow diagrams.
10.General arrangement diagrams.
- Extraction of isometrics and MTO’s.
- Development of detailed diagrams.
11.Pressure drop calculations.
- Straight pipes.
- Valves, fittings and components.
- Pressure Drop in ( Liquid line, Gasses lines and Multi Fluid lines ).
- Fluid flow in Pipe line.
- Types of flows.
12.Pipe supports.
- Importance of Supports.
- Classification of supports. (Rigid, Hanger, Flexible and Restraints).
- Standards.
- Span and specification.
- Applications.
- Representation.
- Rigid ( Shoe, Saddle, Trunnion, Dummy leg, Base adjustment Support and Sleeper ).
- Flexible (Constant load, Variable Load.).
- Restraints (Guide ,Roller, Anchor Supports.)
13.Pipe Racks:.
- Design Concepts.
- Width and height calculations.
- Spacing (spans).
- Pipe arrangements.
- Process Pipelines.
- Utilities.
- Cable Trays.
14.Pipe Thickness calculation: Schedule Selections
15.Pump Head.
- Pump head Calculations
- Closed System and Open system
- Design Concepts
- NPS Ha
- NPS Hr – Cavitations
- Applications
- Pumps Selection
16.Pump Piping Basic: All types of applications, Rooting Concepts of Piping for a pump.
17.Plot Plan
- Equipment layout
- Piping Layout
- Preparation Of equipment layout- Factors consideration, Battery limits and Bund walls
- Concepts
- Sample Layouts
- Importance
18.Piping Layout
- Complete Design Concepts
- Pumps
- Vessels
- Racks / Tracks
- Hazardous
- Head Room clearances
- Control Stations
- Drain Pipelines
- Vent Pipelines
- Process Pipelines
- Safety
- Maintenance
- Operation. etc.,
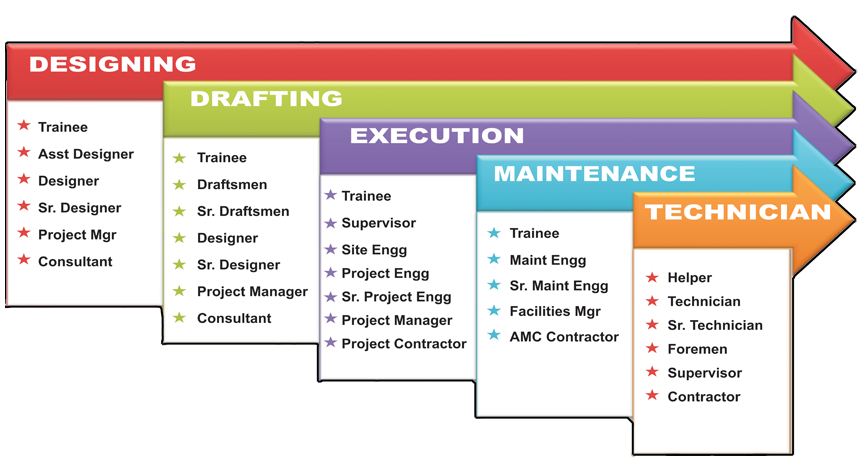
Process piping is a branch of Mechanical engineering which deals with chemical Process, civil layout, Steel and RCC structures, rotating and Static Equipments and piping. Process piping starts with Conceptual formula & Ends with actual piping layout. Process piping is interlinked with varies Disciplines like Chemical, civil, Electrical, Equipment, Structural, firefighting and Instrumentation. Petrochemical, pharmaceuticals, Food and beverages, Cotton, bulk drugs, leather, oil processing, Treatment plants are some examples of Process Industry. In Human Daily Life 80 percent of products are from process industries. In modern days without a process industrial product, Human being can’t proceeds a day. A process piping Engineer can easily perform, Water Distribution, Gas line, Plumbing and Power Industry activities. Process Industry demand is alive till the Human is live on the planet. Engineering diploma /Graduates are suitable for this Industry.
Outcome:
End of the course student get confidence to design of his /her own
- Pipe Material selection according to process fluids.
- Pipe Sizing with respect to Flow rate & Material Flouring
- Get the capabilities’ of making best pipe routing with less power losses.
- Selection of pipe support and pipe racks with complete calculations.
- Pump head calculations and pump selection.
- Lay out design capabilities will be Student assets.
- Enough Drafting practice on isometrics, Detailed Views and Bill of materials.
- Well aware of International piping codes and standards.
- Can read and understand any process diagram and Piping and Instrumentation Diagram(P & ID).
- Gain Capability to Develop Piping lay out from Basic diagram.
- Easy to revise Piping Layout as per the instruction of Stress Analysis
- Full fledge knowledge make them, Well versed to coordinate with other Departments and complete the task in right way.

